
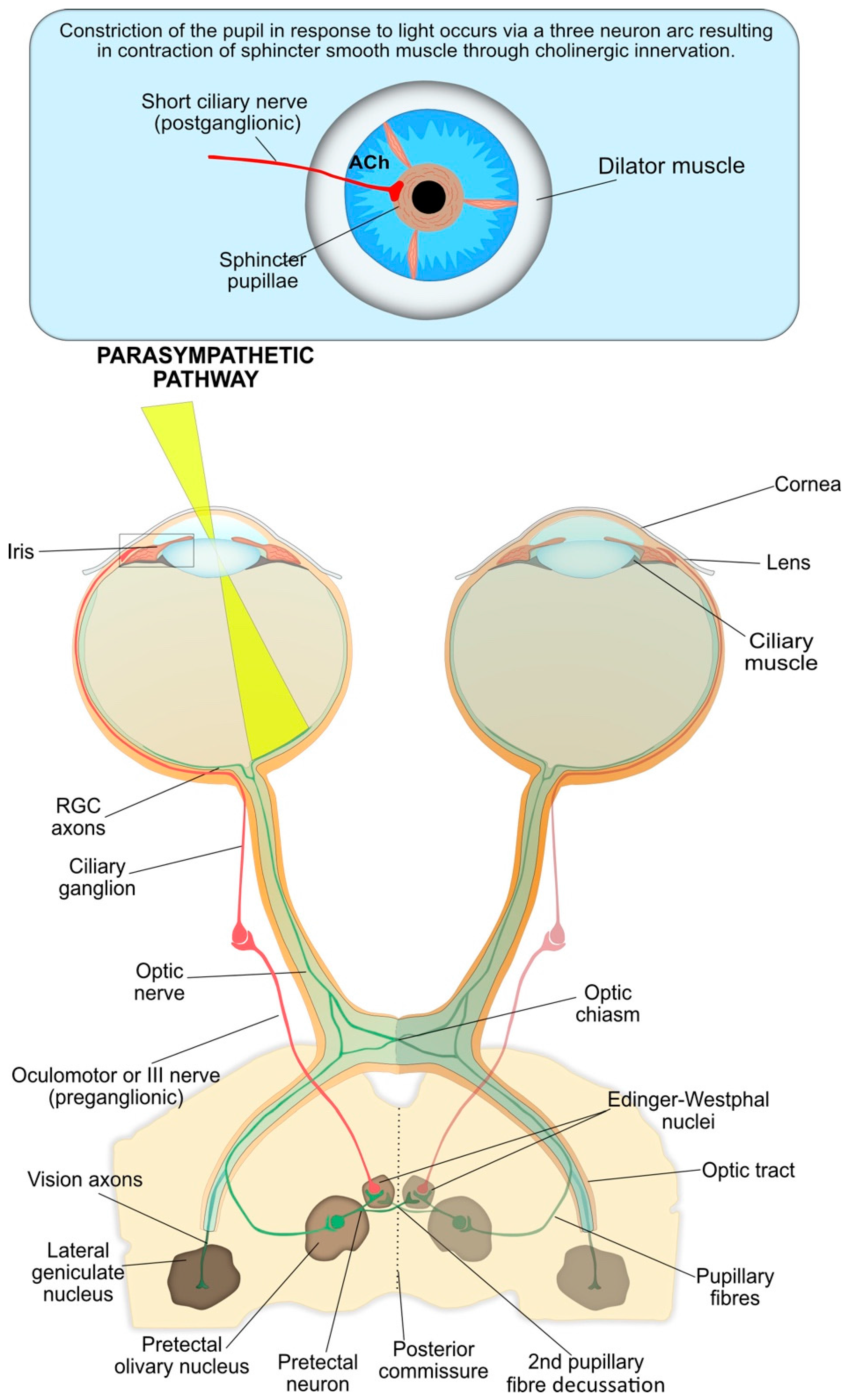
Bilateral stimulation from pre-striate cortex area 19 to the Edinger-Westphal nuclei will do the same trick. Vision is not needed to achieve accommodation. The efferent limb passes from the occipital lobe to the midbrain, where some fibres activate the Edinger-Westphal nucleus as well as the vergence cells in the reticular formation. With accommodation the afferent limb of the reflex passes from the retina to the occipital lobe via the lateral geniculate body. Postganglionic fibres run in the short ciliary nerves and enter the iris to supply the sphincter pupillae (Figure 1). Pre ganglionic parasympathetic fibres enter the oculomotor nerve, leave the branch to the inferior oblique, and synapse in the ciliary ganglion. This pathway results in the direct and indirect light reflex as the input to one optic nerve reaches both Edinger-Westphal nuclei. The contralateral Edinger-Westphal nucleus is reached by way of the posterior commissure. Each pretectal nucleus is linked to its ipsilateral Edinger-Westphal nucleus by internuncial neurons. Fibres leaving the optic chiasm enter both optic tracts and terminate in the pretectal nuclei. The afferent pathway starts in the ganglion cell layer of the retina, which gives rise to the optic nerves. Pupillary constriction is the result of the parasympathetic system activity and is normal in response to two types of stimuli light falling on the retinal photoreceptors and the effort of near reflex and accommodation.Ĭonstriction of the pupils in response to light involves four sets of neurons. The clinical examination of the pupils and pupillary reflexes are crucial in obtaining an accurate diagnosis of a clinical problem. Pupil size is a result of the interplay between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system supplying the intrinsic muscles within the iris, the dilator and sphincter pupillae respectively.
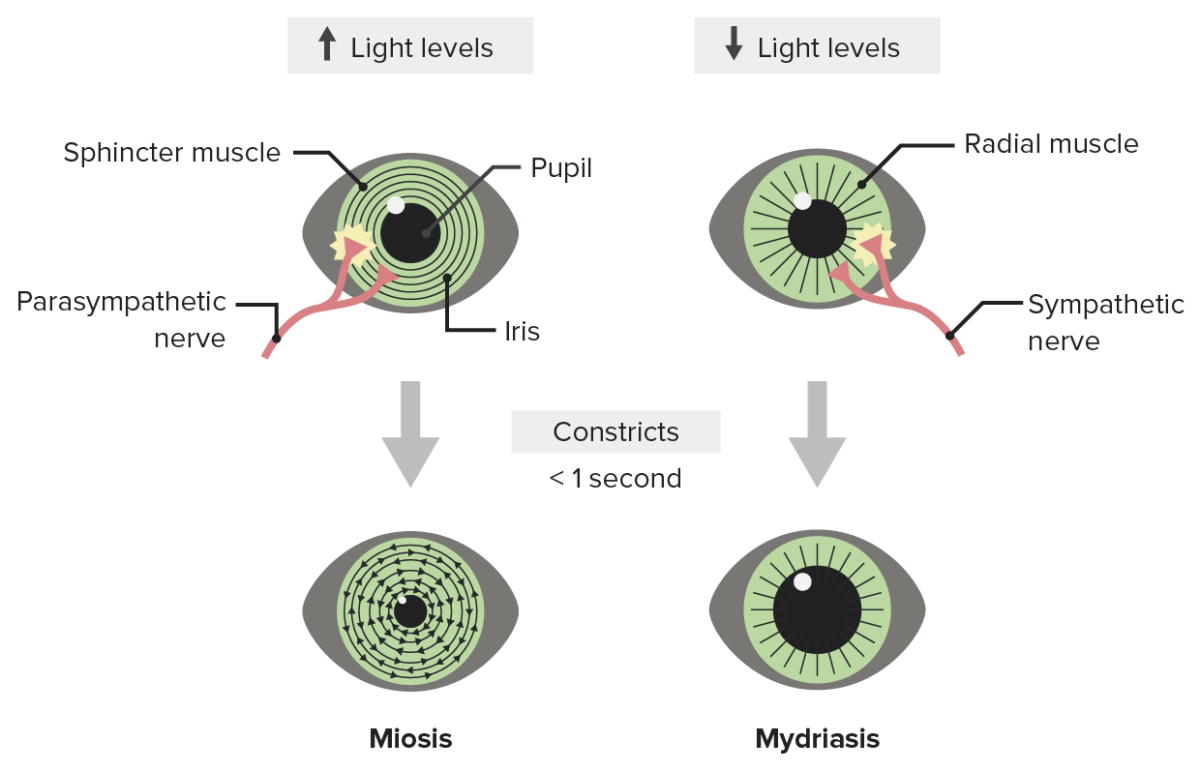
To start at the beginning, the pupil is the central aperture of the iris, its size controlling the amount of light falling on the retina, varying in diameter from about 1-8mm. It is a skill required in eye casualty, clinics and perhaps most importantly, exams. Understanding pupillary reactions is vital in understanding basic neuro-opthalmology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
